Caste is a social and cultural institution that has been prevalent in India for more than 2,000 years. It is a system of social stratification that divides people into different groups based on their birth, occupation, and social status. The caste system is based on the idea that people are born into a particular caste and cannot change it during their lifetime. The caste system is also known as Varna in Hinduism, which means color.
The caste system is not unique to India and has been observed in other parts of the world as well. However, the Indian caste system is particularly rigid and hierarchical. It has had a profound impact on Indian society, shaping its culture, politics, and economy.
Origin of Caste
The origins of the caste system in India are unclear, but it is believed to have developed around the time of the Aryans. The Aryans were a group of people who migrated to India from Central Asia around 1500 BCE. They brought with them their own customs and beliefs, which merged with the existing culture of India.
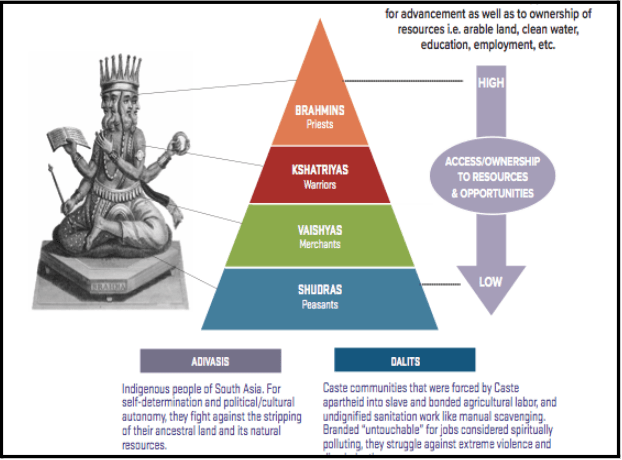
The caste system evolved over time, with different castes being added or removed. The four main castes in Hinduism are Brahmins, Kshatriyas, Vaishyas, and Shudras. The Brahmins were the highest caste and were responsible for religious rituals and teaching. The Kshatriyas were warriors and rulers. The Vaishyas were merchants and traders, while the Shudras were manual laborers.
In addition to these four main castes, there were also other castes that were considered lower than the Shudras. These castes were known as the Dalits or the “untouchables.” They were considered to be outside the caste system and were subjected to extreme discrimination and oppression.
Meaning of Caste
Caste is a complex social and cultural institution that has various meanings and implications. At its core, caste is a system of social stratification that divides people into different groups based on their birth, occupation, and social status. Caste is also linked to religion, with each caste having its own set of customs, rituals, and beliefs.
Caste is a deeply ingrained concept in Indian society and affects every aspect of life, including marriage, education, and employment. People are expected to marry within their own caste, and inter-caste marriages are still frowned upon. The caste system also affects education and employment opportunities, with people from lower castes often facing discrimination and lower social mobility.
The caste system has also had a significant impact on politics in India. Political parties often align themselves with specific castes to gain their support. Caste-based politics has been a major factor in Indian politics, and has led to conflicts and tensions between different castes.
Impact of Caste
The impact of caste on Indian society is far-reaching and complex. Caste has led to social stratification and inequality, with people from lower castes facing discrimination and oppression. The caste system has also created a sense of hierarchy and superiority among different castes, which has led to conflicts and violence.
Despite efforts to abolish caste discrimination, it continues to be a pervasive social issue in India. The Indian government has introduced several laws and policies to promote equality and social justice, but the implementation of these laws has been slow and ineffective.
One of the major issues with the caste system is the practice of untouchability. The Dalits or the “untouchables” are often subjected to extreme discrimination and are considered to be outside the caste system. They are not allowed to enter temples, schools, or other public places, and are often subjected to violence and abuse.
Another issue with the caste system is the impact it has on inter-caste marriages. People are expected to marry within their own caste, and inter-caste marriages are still considered taboo. This has led to a lack of social mobility and has perpetuated the caste system.
The caste system has also had an impact on the economy of India. The lower castes, particularly the Dalits, have traditionally been engaged in manual labor and have been excluded from higher-paying jobs and education opportunities. This has led to a lack of economic opportunities and perpetuated the cycle of poverty.
Efforts to Abolish Caste Discrimination
Efforts to abolish caste discrimination in India have been ongoing for centuries. The Indian government has introduced several laws and policies to promote equality and social justice. The Indian Constitution prohibits discrimination based on caste, and the government has introduced several affirmative action programs to promote the social and economic welfare of lower castes.
In addition to government efforts, civil society organizations and activists have also played a key role in promoting caste equality. Dalit movements and organizations have been particularly active in advocating for the rights of lower castes and for the abolition of the caste system.
Despite these efforts, caste discrimination and inequality continue to be pervasive in Indian society. The implementation of laws and policies aimed at promoting equality has been slow and ineffective, and the caste system remains deeply ingrained in Indian culture and society.
Conclusion
Caste is a complex social and cultural institution that has had a profound impact on Indian society. The caste system is based on the idea that people are born into a particular caste and cannot change it during their lifetime. The caste system has led to social stratification, inequality, and discrimination, particularly against lower castes such as the Dalits.
Efforts to abolish caste discrimination in India have been ongoing for centuries, but the caste system remains deeply ingrained in Indian society. The Indian government has introduced several laws and policies to promote equality and social justice, but the implementation of these laws has been slow and ineffective. Civil society organizations and activists have also played a key role in advocating for the rights of lower castes and for the abolition of the caste system.
Is caste discrimination still prevalent in India?
Yes, caste discrimination continues to be a pervasive social issue in India, particularly against lower castes such as the Dalits.
What is the impact of caste on Indian society?
The impact of caste on Indian society is far-reaching and complex. Caste has led to social stratification and inequality, with people from lower castes facing discrimination and oppression. The caste system has also created a sense of hierarchy and superiority among different castes, which has led to conflicts and violence.
What are the efforts to abolish caste discrimination in India?
Efforts to abolish caste discrimination in India have been ongoing for centuries. The Indian government has introduced several laws and policies to promote equality and social justice, and civil society organizations and activists have also played a key role in advocating for the rights of lower castes and for the abolition of the caste system.
What is the impact of the caste system on inter-caste marriages?
The caste system has led to a lack of social mobility and has perpetuated the cycle of poverty. People are expected to marry within their own caste, and inter-caste marriages are still considered taboo.
What is the impact of the caste system on the economy of India?
The lower castes, particularly the Dalits, have traditionally been engaged in manual labor and have been excluded from higher-paying jobs and education opportunities. This has led to a lack of economic opportunities and perpetuated the cycle of poverty.