Batik is a traditional textile art form that is most commonly associated with Indonesia, but also practiced in other countries in Southeast Asia, such as Malaysia and Singapore. The word “batik” comes from the Javanese word “ambatik” which means “to write” or “to dot”.
The process of creating batik involves using a tool called a tjanting (a small copper stamp with a spout) to apply wax to a piece of fabric. The fabric is then dyed, and the waxed areas resist the dye, creating a pattern. The process is repeated multiple times with different colors, each time covering the areas that have already been dyed with wax. Finally, the wax is removed, revealing the final pattern.
Traditionally, batik was used to make clothing, such as sarongs, scarves and shirts, but today it is also used to make wall hangings, tablecloths and other decorative items. The designs used in batik are often symbolic and have cultural significance. Each region in Indonesia has its own unique style of batik.
Batik is also considered as an UNESCO intangible cultural heritage in 2009. Today, batik is not only used for traditional purpose but also for modern fashion, interior design and many other creative fields. The technique of batik is also being adapted to other forms of art such as painting and printmaking.
Introduction
Definition of Batik
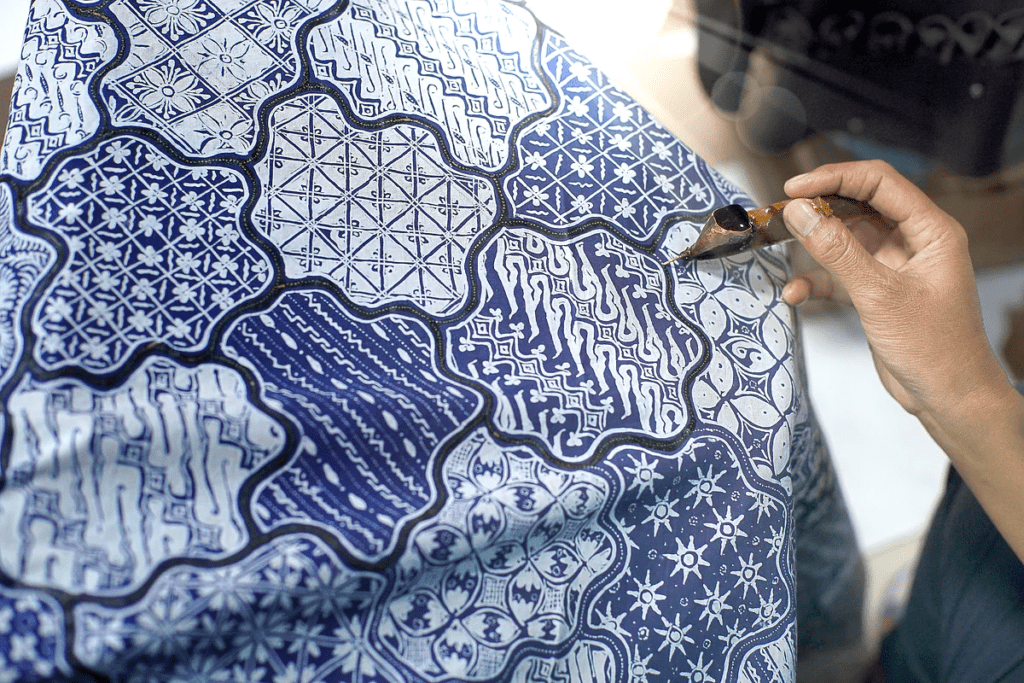

Batik is a traditional textile art form that involves creating patterns and designs on fabric using a wax-resist dyeing technique. The word “batik” comes from the Javanese word “ambatik” which means “to write” or “to dot”. The process of batik includes coating the fabric with wax, and then dyeing it. The areas of the fabric covered in wax will resist the dye, creating a pattern on the fabric. The process can be repeated multiple times to create intricate designs, by applying wax in different areas and dyeing the fabric with different colors. The final step is to remove the wax from the fabric, revealing the final design. Batik is particularly associated with Indonesia, but it also practiced in other Southeast Asian countries such as Malaysia and Singapore.
Origins and history of Batik
The origins and history of batik are not well-documented and can be traced back to ancient civilizations, but it is most strongly associated with the island of Java in Indonesia. Batik is believed to have been brought to the island by traders from India and China, who would have used the technique to decorate fabrics for trade.

Batik became a traditional art form in Java and it was mainly used to make clothing, such as sarongs and kain (traditional Javanese cloth). It was also used to make ceremonial garments for the royal courts. The designs used in traditional batik were often symbolic and had cultural significance. Each region in Java had its own unique style of batik.
During the colonial era, the Dutch banned the use of traditional batik to protect their own textile industry. However, the art form managed to survive and continued to be passed down through the generations.
In the 20th century, batik experienced a resurgence in popularity, particularly among the educated elite and artists. Today, batik is considered as an UNESCO intangible cultural heritage in 2009. It is not only used for traditional purpose but also for modern fashion, interior design and many other creative fields. The technique of batik is also being adapted to other forms of art such as painting and printmaking.
Regional variations and styles of Batik
There are many regional variations and styles of batik found in Indonesia and other Southeast Asian countries where it’s practiced. Each region has its own unique style, influenced by the local culture, history and natural environment. Some of the most notable regional variations and styles of batik include:
- Javanese Batik: Javanese batik is considered to be the most traditional and authentic style of batik. It is characterized by its intricate designs, often featuring symbolic motifs such as the keprah (a pair of hands) and the parang rusak (broken sword). The most famous Javanese batik is the batik from the city of Yogyakarta and Surakarta.
- Sumatran Batik: Sumatran batik is known for its bold, geometric designs and bright colors. The batik from the city of Palembang is particularly notable for its use of gold and silver thread.
- Balinese Batik: Balinese batik is known for its use of natural dyes and simple, geometric patterns. The batik from the island of Bali is characterized by its use of traditional motifs such as the Barong (a mythical lion-like creature) and the Kebo (an ox-like creature).
- Malay Batik: The batik from Malaysia and Singapore is known for its use of bright colors and bold, floral designs. The batik from the state of Kelantan in Malaysia is particularly notable for its intricate and delicate designs.
- Chinese Batik: Chinese batik, also known as Cantonese batik, is a variation of batik that was developed in China’s southern province of Guangdong. It is characterized by its use of bright colors and bold, floral designs.
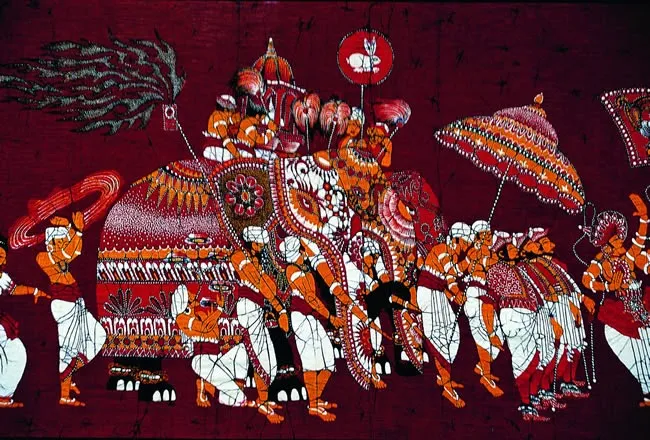

By studying these regional variations and styles of batik, one can gain a deeper understanding of the cultural and historical influences that have shaped the art form over time.
The Process of Creating Batik
Tools and materials used
The tools and materials used in the process of creating batik vary depending on the technique and style being used, but some of the most commonly used tools and materials include:
- Fabric: The most common fabric used for batik is a cotton, but other fabrics such as silk and rayon can also be used.
- Wax: The traditional wax used in batik is made from the resin of the cand tree, which is native to Indonesia. The wax is typically melted and then applied to the fabric using a tool called a tjanting.
- Tjanting: A tjanting is a small copper stamp with a spout that is used to apply the wax to the fabric. It is held like a pen and the wax is poured into the tjanting’s reservoir and then applied onto the fabric.
- Dyes: The dyes used in batik can be made from natural materials such as leaves, bark, and roots, or from chemical dyes. The dyes are typically applied to the fabric after it has been waxed, and the areas covered in wax will resist the dye, creating the pattern.
- Pot: A pot is used to heat the wax, so it can be applied to the fabric.
- Brushes: The brushes are used to apply the dyes on the fabric.
- Combs: The combs are used to create fine lines and dots on the fabric.
- Tongs: Tongs are used to handle the fabric when it is being dyed.
- Scissors: Scissors are used to cut the fabric to the desired size.
- Stove: A stove is used to heat the dyes.
- Clamps: Clamps are used to hold the fabric in place while it is being dyed.
- Boiler: A boiler is used to melt the wax.
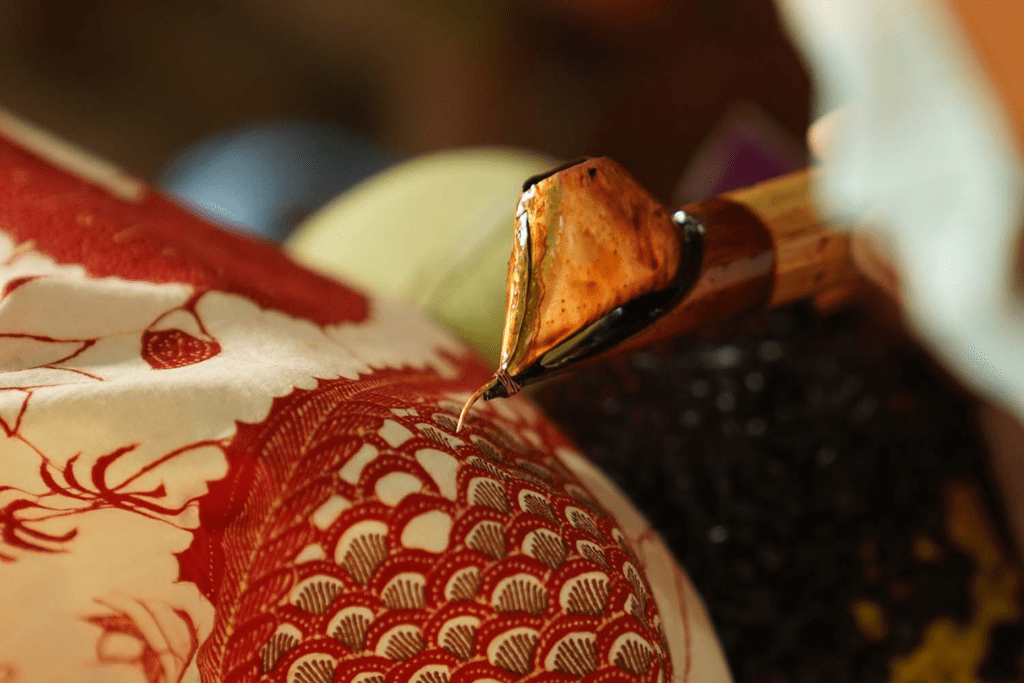

By using these tools and materials, the artist can create intricate designs and patterns on the fabric, creating a unique and beautiful piece of batik.
Techniques of applying wax and dying
The techniques of applying wax and dying in batik can vary depending on the style and tradition of the artist, but some of the most common techniques include:
- Tjanting: The tjanting is a tool that is used to apply the wax to the fabric. The wax is poured into the tjanting’s reservoir and then applied onto the fabric in the desired pattern. This technique is used to create fine lines and detailed patterns on the fabric.
- Canting: Canting is similar to tjanting but it is smaller and uses a metal nib instead of a copper stamp. It is used to apply wax in small, detailed areas, such as for making dots.
- Cap: The cap technique is used to apply wax in large areas of the fabric. The artist dips a copper stamp (cap) into the melted wax and then stamps it onto the fabric, creating a large area of wax. This technique is used to create larger patterns and backgrounds on the fabric.
- Manual Wax-Resist: This technique involves using a brush to paint the wax onto the fabric in the desired pattern. This technique is mainly used in creating traditional Javanese batik.
- Batik Painting: This technique is similar to watercolor painting. The wax is applied to the fabric in the desired pattern and then the fabric is dyed. The wax resists the dye, creating a pattern on the fabric. This technique is mainly used in creating traditional Javanese batik.
- Rolling: Rolling is a technique where the wax is applied to the fabric using a roller. This technique is mainly used in creating traditional Javanese batik.
Once the wax has been applied to the fabric, the fabric is then dyed. The areas covered in wax will resist the dye, creating the pattern. The process can be repeated multiple times, with different colors and wax patterns to create intricate designs.
It’s important to note that these are just some examples of the techniques that can be used, and there are many other variations and styles of applying wax and dying.
The meaning behind traditional Batik designs
The traditional designs used in batik often have cultural and symbolic meanings, which reflect the beliefs and values of the culture from where it originates. Many traditional batik designs are inspired by nature, and they often depict plants, animals and other elements of the natural world. Some of the most common motifs found in traditional batik designs include:
- Floral motifs: Flowers are commonly used in batik designs and they often have symbolic meanings. For example, the lotus flower is a symbol of purity and enlightenment, while the hibiscus is a symbol of love and beauty.
- Animal motifs: Animals are also commonly used in batik designs and they often have symbolic meanings. For example, the Barong, which is a mythical lion-like creature, is a symbol of good fortune and protection, while the Kebo, which is an ox-like creature, is a symbol of strength and power.
- Geometric motifs: Geometric shapes are commonly used in batik designs, and they often have symbolic meanings. For example, the parang rusak (broken sword) is a symbol of protection, while the keprah (pair of hands) is a symbol of unity and harmony.
- Human figures: Human figures are also commonly used in batik designs, and they often have symbolic meanings. For example, Wayang (shadow puppet) figures are used to tell stories and convey moral messages.
- Nature motifs: Nature is a common theme in batik designs, and it often depicts trees, leaves, and other natural elements. These motifs often have symbolic meanings, for example, the Tree of Life is a symbol of growth and nourishment.
By understanding the meaning behind traditional batik designs, one can gain a deeper appreciation for the art form and the culture from which it originates.
It’s important to note that the meaning of the designs can vary depending on the context and the culture. It’s also important to note that the meaning of the designs can be different from the original meaning and can be adapted by the artist or the culture that uses it.
Contemporary Batik
Modern adaptations of Batik
In recent years, batik has undergone a resurgence in popularity and has been adapted to modern styles and techniques. Some examples of modern adaptations of batik include:
- Contemporary Batik Art: Many artists have started to experiment with batik as a medium for fine art, creating abstract and modern compositions using traditional techniques.
- Fashion and Textile Design: Batik has been adapted to create a variety of fashion and textile products such as clothing, accessories, and home décor items. Many designers and fashion brands have started to incorporate batik in their collections, giving it a modern twist.
- Digital Batik: Some artists have started to use digital techniques to create batik designs. This allows for more precise and intricate designs and also allows for the use of a wider range of colors.
- Batik Printing: Some artists have started to use printing techniques to reproduce batik designs on a variety of materials such as paper, fabrics, and even ceramics.
- Fusion Batik: Some artists have started to combine traditional batik techniques with other art forms such as painting, drawing, and printmaking to create unique and modern styles.
These modern adaptations of batik have helped to make the art form more accessible and relevant to a wider audience. It has also helped to preserve traditional batik techniques and keep the art form alive.
It’s important to note that while these modern adaptations may have changed the way batik is created and perceived, it is still an important part of the cultural heritage and should be respected.
Use of Batik in fashion and interior design
The use of batik in fashion and interior design has become increasingly popular in recent years, as it allows for the incorporation of traditional art and culture into modern designs. Some examples of how batik is used in fashion and interior design include:
- Clothing: Batik is often used to create a variety of clothing items such as dresses, skirts, pants, and shirts. The designs are often adapted to suit modern fashion trends, while still preserving the traditional elements of the art form.
- Accessories: Batik is also used to create a variety of accessories such as scarves, bags, and shoes. These items are often used as statement pieces to add a touch of traditional culture to an outfit.
- Home décor: Batik is also used in home décor, such as wall hangings, tablecloths, and cushion covers. These items can add a traditional touch to a room and can also be used as conversation pieces.
- Furniture: Furniture can be designed with batik motifs, using the technique of batik printing, for example.
- Interior design: batik can also be used in interior design projects, such as creating custom murals, wallpapers, and other decorative elements.
The use of batik in fashion and interior design not only adds a unique and traditional element to the designs but also helps to preserve and promote the art form. Batik has been used in interior design and fashion for a long time, and it can be a great way to bring a touch of cultural heritage and artistic expression to a space or an outfit. It can also be a great way to support local artisans and communities who are keeping the traditional batik techniques alive. Additionally, the use of batik in fashion and interior design can also help to introduce new audiences to the art form and promote cultural awareness and understanding.
Batik in other forms of art
The technique of batik has been adapted to other forms of art beyond textiles and fashion, such as:
- Painting: Many artists have started to use batik as a medium for painting, creating abstract and modern compositions using traditional wax-resist dyeing techniques.
- Printmaking: Some artists have started to use batik as a medium for printmaking, creating prints using traditional batik techniques and designs.
- Photography: Batik can also be used as a background or a subject in photography to create unique and artistic compositions.
- Sculpture: Sculptors have started to use batik as a medium for sculpture by creating three-dimensional forms using batik techniques.
- Installation art: Batik can also be used as a medium for installation art, creating large-scale installations that incorporate traditional batik techniques and designs.
- Digital Art: Some artist have started to use digital software to create batik designs, this allows for more precise and intricate designs, and also allows for the use of a wider range of colors.
These adaptations demonstrate the versatility and adaptability of batik as an art form. It allows the traditional technique to be used in new and innovative ways, which helps to keep the art form alive and relevant to a wider audience.

Conclusion
In 2009, UNESCO recognized the traditional art of batik as a Masterpiece of Oral and Intangible Heritage of Humanity. This recognition is awarded to cultural practices that are considered to be of outstanding universal value and that help to promote cultural diversity.
The recognition by UNESCO highlights the importance of preserving and promoting the traditional art of batik, as well as the culture and heritage from which it originates. It also helps to raise awareness about the art form and its cultural significance, which can help to attract more support and funding for its preservation.
The recognition also brings attention to the need for education and training in the traditional techniques of batik, so that it can be passed on to future generations. This is important as traditional batik is a technique passed down from generation to generation, it is considered as an important aspect of cultural heritage and identity for many communities.
UNESCO also encourages the promotion of the traditional batik in the context of contemporary art and design, in order to keep the art form alive and relevant to a wider audience. This recognition is a great way to celebrate the traditional art of batik and the culture and heritage from which it originates and a way to help preserve it for future generations.
Batik plays an important role in preserving cultural heritage by providing a link to the past and keeping traditional techniques and designs alive. The traditional art of batik is deeply rooted in the culture, history and beliefs of the communities where it is practiced. It is a way to express their identity and cultural heritage and to tell their stories.
The traditional techniques and designs used in batik are passed down from generation to generation, and this helps to keep the art form and the culture alive. By preserving traditional batik techniques and designs, we are also preserving the cultural heritage and history that they represent.
The recognition of batik as a UNESCO intangible cultural heritage also helps to preserve the art form by raising awareness and support for its preservation. This recognition brings attention to the need for education and training in traditional batik techniques and helps to ensure that the art form is passed on to future generations.
Moreover, the use of batik in modern fashion and interior design, and other forms of art, helps to keep the art form relevant and alive. This allows traditional techniques and designs to be adapted to modern styles and trends, which can attract a wider audience and promote cultural awareness and understanding.
In short, batik is more than just a textile art form, it’s a way to preserve cultural heritage and identity, and to tell stories of the past. It’s an important aspect of cultural heritage and identity for many communities and it’s crucial to preserve it for future generations. By preserving traditional batik techniques and designs, we are also preserving the cultural heritage and history that they represent. In addition, by promoting the use of batik in modern contexts, we are keeping the art form alive and relevant, and attracting new audiences to appreciate and learn about the cultural significance of batik.
Moreover, by recognizing batik as a UNESCO intangible cultural heritage, it also helps to promote the sustainable development of communities who are practicing the art form, by providing them with opportunities to earn a livelihood through their traditional skills, and by encouraging the participation of young people in the transmission of the knowledge and skills.
In conclusion, the significance of batik in preserving cultural heritage is multi-fold, it helps to preserve traditional techniques, designs, and culture, promotes cultural awareness and understanding, and provides opportunities for the sustainable development of communities who are practicing the art form. It’s an important aspect of cultural heritage and identity for many communities and it’s crucial to preserve it for future generations.
The future of batik looks promising as it continues to evolve and adapt to new styles and trends. The use of batik in modern fashion and interior design, as well as other forms of art, has helped to make the art form more accessible and relevant to a wider audience.
The recognition of batik as a UNESCO intangible cultural heritage has also helped to raise awareness and support for its preservation, which can help to attract more funding and resources for education and training in traditional batik techniques. This will ensure that the art form is passed on to future generations and can continue to be practiced and appreciated.
Digital technology also plays a role in the future of batik, as more artists are using digital tools to create batik designs. This allows for more precise and intricate designs and also allows for the use of a wider range of colors. Additionally, the use of digital tools allows for the creation of digital prints, which can be used in fashion and interior design, making it more accessible to a wider audience.
In addition, the use of batik in modern art forms, such as painting and sculpture, can also help to attract new audiences and promote cultural awareness and understanding. This can help to keep the art form relevant and alive, and attract new audiences to appreciate and learn about the cultural significance of batik.
Overall, the future of batik looks promising as it continues to evolve and adapt to new styles and trends, and with the help of digital technology, it has the potential to reach a wider audience and promote cultural awareness and understanding.