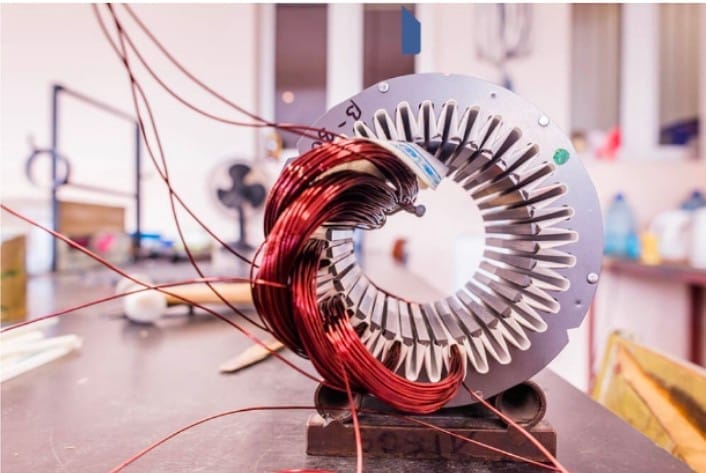
Introduction
In the realm of electric motors, efficiency and performance are paramount. One critical component that significantly influences these factors is the winding material used in the motor. Among various winding configurations, hairpin motor windings have gained prominence for their superior conductivity and thermal properties.
Understanding Hairpin Motor Windings
Hairpin motor windings, also known as hairpin windings, refer to a specific configuration of conductive wires within an electric motor. Unlike traditional round wire windings, hairpin winding feature flat, rectangular-shaped conductors that are bent into a hairpin-like shape. This design offers several advantages, including reduced resistance, improved heat dissipation, and increased power density.
The Significance of Material Selection
The material used for hairpin motor windings plays a crucial role in determining the overall performance and efficiency of the motor. Key factors to consider when selecting winding materials include electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, mechanical strength, and cost-effectiveness. By choosing the appropriate material, engineers can optimize motor performance while ensuring reliability and longevity.
Copper: The Gold Standard
Copper stands as the most commonly used material for hairpin motor windings due to its exceptional electrical conductivity. With a conductivity rating significantly higher than other metals, copper minimizes power losses within the motor, leading to improved efficiency. Additionally, copper exhibits excellent thermal conductivity, facilitating efficient heat dissipation and preventing overheating during operation.
Aluminum: A Lightweight Alternative
While copper remains the preferred choice for hairpin motor windings, aluminum offers a viable alternative, particularly in applications where weight reduction is critical. Although aluminum has lower conductivity compared to copper, advancements in alloy compositions have improved its electrical properties. Additionally, aluminum’s lower density makes it an attractive option for high-speed and aerospace applications where weight savings are paramount.
Copper-Clad Aluminum (CCA): Finding the Middle Ground
Copper-clad aluminum (CCA) combines the conductivity of copper with the lightweight properties of aluminum. In CCA windings, aluminum serves as the core material, while a thin layer of copper is applied through a cladding process. This hybrid construction provides a balance between conductivity and weight, making CCA suitable for applications that prioritize both performance and cost-effectiveness.
Copper vs. Aluminum: A Comparative Analysis
When deciding between copper and aluminum for hairpin motor winding, engineers must weigh the advantages and limitations of each material. Copper offers superior conductivity and thermal properties, making it ideal for high-performance applications where efficiency is paramount. However, copper’s higher cost and heavier weight may pose challenges in certain scenarios. On the other hand, aluminum offers a lightweight solution with adequate conductivity, making it suitable for applications where weight savings are critical, despite its slightly lower performance compared to copper.
Future Trends and Innovations
As technology advances, researchers continue to explore new materials and manufacturing techniques to further enhance the performance of hairpin motor windings. Emerging trends include the development of composite materials, such as carbon nanotubes and graphene, which offer unprecedented levels of conductivity and strength. Additionally, additive manufacturing processes, such as 3D printing, enable the production of intricate winding designs with optimized performance characteristics.
Conclusion
Material selection plays a pivotal role in the design and performance of hairpin motor windings. By carefully considering factors such as electrical conductivity, thermal properties, and cost-effectiveness, engineers can maximize the efficiency and reliability of electric motors across a wide range of applications. Whether opting for the tried-and-true conductivity of copper or the lightweight versatility of aluminum, the choice of winding material shapes the future of electric motor technology, driving innovation and sustainability in industries worldwide.